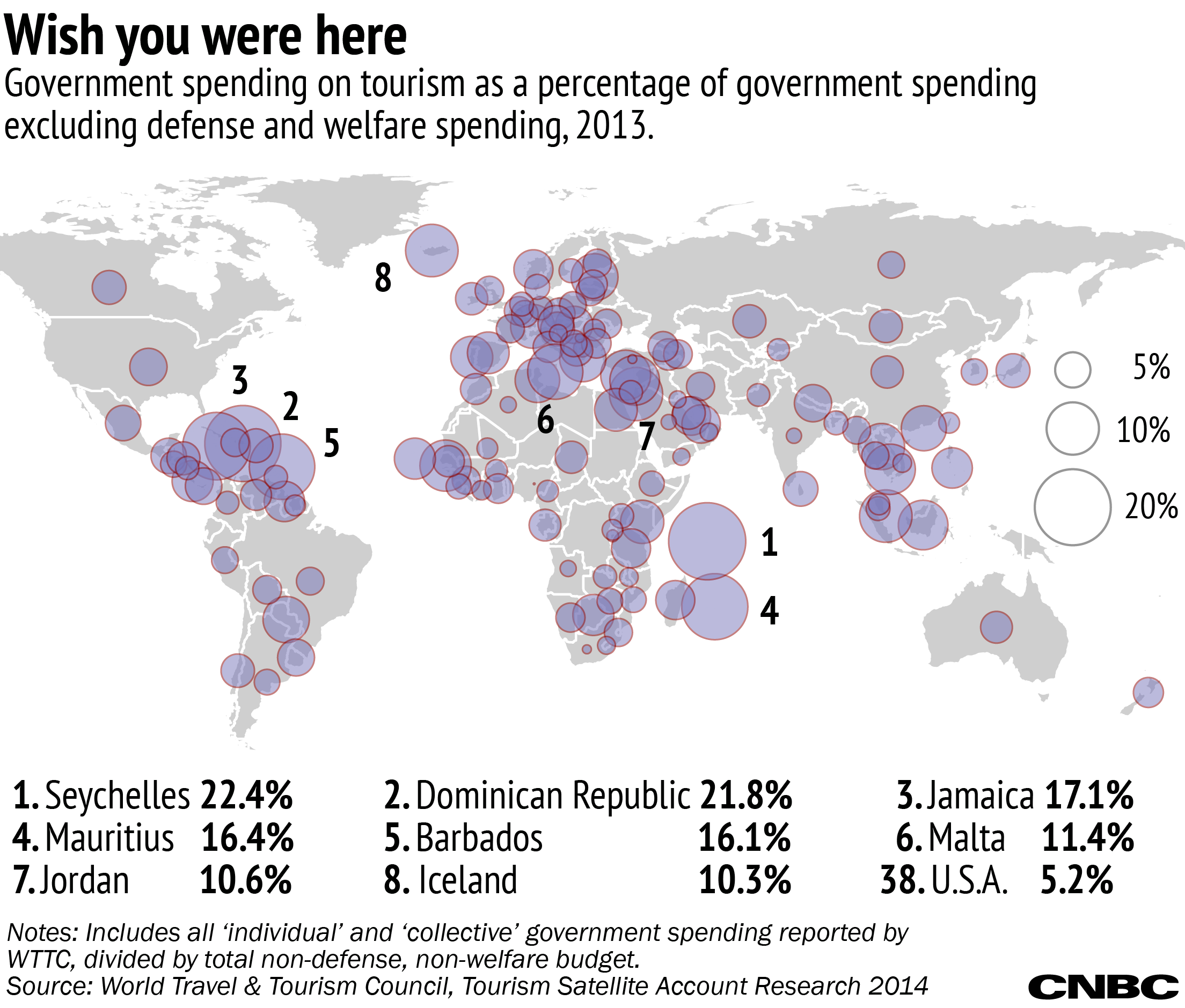
Since its conception, many countries in the developed world and particularly in Africa, have embraced and encouraged ecotourism as a means of attracting foreign investment and exchange. Originally conceived in response to declining environmental and economic conditions throughout the developing world, ecotourism and other forms of sustainable travel not only have low impact on the environment, but also contribute to the economy. However, Nigeria despite its rich biodiversity and extensive ecosystem is unfortunately yet to actually tap into this economy ueing venture, unlike its other African counterparts such as South Africa, Ghana, Kenya and Ethiopia, among others, who inarguably enrich their economy through wildlife usinf tourism. It is one of the government using ecotourism as a way to make money growing sectors in the travel industry, with a growth rate of 10 to 30 per cent. Tourism itself is the biggest sector of business in the world economy, responsible for over million jobs and 10 per cent of the gross domestic product GDP worldwide. According to TIES, 83 per cent of developing countries rely on ecotourism as a major export, while others such as Costa Rica, Ecuador, Nepal, Kenya, Madagascar and Antarctica, rely on ecotourism as the major contributory govfrnment in their GDP and employment level calculations. The eighth, Yankari Game Reserve was upgraded to a national park inalthough it was later handed over to the Bauchi State Government in June Responsible for preserving, enhancing, protecting and managing vegetation and wild animals in the national parks of Nigeria, the NNPS is a parastatal under the Federal Ministry of the Environment. The uniqueness of the Ikogosi Warm Springs in Ekiti State is in the flow of its water, where both warm and cold spring flow side by side, each maintaining its thermal properties.
These destinations represent different stages of tourism development. The assessment shows that the development of ecotourism has a dilemma character. Compared to alternative land-use options, ecotourism remains a promising development strategy. However, it should be embedded in a broader process of capacity building. Since the mids, Costa Rica has been very successful in attracting tourists. Annually, more than one million tourists visit the country, and the tourism industry has an annual turnover of over 1, million dollars ICT The country has especially much to offer to nature enthusiasts. Ecotourism has been promoted as a non-consumptive use of nature and as a possible win—win development strategy, especially for underdeveloped areas a. Boo ; Honey b ; Weaver Ecotourism should not only conserve the environment, but also improve the welfare of local people Edwards et al. It should generate money in an ecologically and socially friendly way than other forms of land exploitation. An increase in the numbers of visitors for instance calls for waste processing facilities that are often missing Boo ; Hardy et al.
So, the questions can be raised whether it is wise for Costa Rica and other developing countries to focus on ecotourism as a development strategy, or whether these countries face challenges they are not up to. In the Manuel Antonio region, tourism development started in the s, followed in the s by initiatives in Monteverde and Tortuguero. Following Stern et al. We presume that a larger scale will give greater benefits, but also more drawbacks. In the end, we expect the drawbacks to dominate the benefits in case of large-scale tourism.
Discover the world’s research
Advantages of Ecotourism Photo:. A vacation at an ecotourism site can give a warm, fuzzy feeling. Ecotourists learn about the ecosystems, traditions and cultures of their destination without missing out on adventure, excitement and relaxation. For local communities, it’s a win-win experience. Ecotourism provides support through employment and other means, but not at the expense of the local environment. Search listings at reputable websites before booking a vacation to avoid unscrupulous companies that don’t offer genuine ecotourism opportunities. Ecotourism helps protect natural habitats and pristine environments. The wealth of poorer countries is often tied up in natural resources like forests, minerals and land that could be used for agriculture.
Recommendations
Ecotourism helps in environmental protection, wildlife conservation, poverty alleviation and socio-economic development. It affects environmental, social and economic components of the community and the whole country. It has different forms which are named according to the preference of the country. Developed as well as developing countries , such as Nepal, are promoting ecotourism for sustainable development of the nation. Different methodologies are applied throughout the world by different researchers for assessing ecotourism. This chapter focuses on review of ecotourism researches throughout the world.
South Australian tourism strategy and the role of ecotourism. The tourists stay in locally-owned hotels and can sold by the local community. January 20, By subscribing you agree to our Privacy Policy. Natural resource management can be utilized as a specialized tool for the development of ecotourism. Nowadays, an increasing number of people want their holiday to have a positive impact on local people and ecotourism does this. United Kingdom: John Wiley and Sons. Ecotourism: the uneasy alliance. Ecotourism is a late 20th-century neologism compounded from eco- and tourism. Only local guides are employed to show the tourists the sights and explain the different customs and culture.
Ecotourism and the Environment
For example, the percentage of money from eco holidays that goes to the local community is usually much higher then from traditional package holidays. Because governmwnt prestige and conspicuousness, the construction of an attractive visitor’s center at an ecotourism site may take precedence over more pressing environmental concerns like acquiring habitat, protecting endemic species, and removing invasive ones. Ecotourism uxing responsible travel to natural areas, travel which conserves the environment and improves the well-being aay local people. When such investments are required, it is crucial for communities to find a company or non-governmental organization that reflects the philosophy of ecotourism; sensitive to their concerns and willing to cooperate at the expense of profit. Following a complete ban on commercial logging the indigenous people of the Yunnan region now see little opportunity for economic development. There is also usually a strong educational component associated with ecotourism, which also helps, but is not mandatory. However, when used properly, ecotourism can make a difference and help species in need.
Ecotourism: potentials and pitfalls
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving visiting fragile, pristine, and relatively undisturbed natural areas, intended as a low-impact and often small scale alternative to standard commercial mass tourism.
It means responsible travel to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Since the s, ecotourism has been considered a critical endeavor by environmentalists, so that future generations may experience destinations relatively untouched by human intervention.
Generally, ecotourism deals with interaction with biotic components of the natural environments. Ecotourism typically involves travel to destinations where florafaunaand cultural heritage are the primary attractions.
Ecotourism is intended to offer tourists an insight into the impact of human beings on the environment and to foster a greater appreciation of our natural habitats. Responsible ecotourism programs include those that minimize the negative aspects of conventional tourism on the environment and enhance the cultural integrity of local people.
Therefore, in addition to evaluating environmental and cultural factors, an integral part of ecotourism is the promotion of recyclingenergy efficiencywater conservationand creation of economic opportunities for local communities. Many consider the term «ecotourism», like » sustainable tourism «, an oxymoron. Like most forms of tourism, ecotourism generally depends on air transportation, which contributes to global climate change. Additionally, «the overall effect of sustainable tourism is negative where like ecotourism philanthropic aspirations mask hard-nosed immediate self-interest.
Ecotourism is tourism which is conducted responsibly to conserve the environment and sustain the well-being of local people. The International Ecotourism Society defines ecotourism as «responsible travel to natural areas that conserves the environment, sustains the well-being of local people, and involves interpretation and education».
For many countries, ecotourism is not simply a marginal activity to finance protection of the environmentbut a major industry of the national economy. For example, in Costa RicaEcuadorNepalKenya, Madagascar and territories such as Antarcticaecotourism represents a significant portion of the gross domestic product and economic activity.
Ecotourism is often misinterpreted as any form of tourism that involves nature see Jungle tourism. Self-proclaimed practitioners and hosts of ecotourism experiences assume it is achieved by simply creating destinations in natural areas. According to critics of this commonplace and assumptive practice, true ecotourism must, above all, sensitize people to the beauty and the fragility of nature.
Although academics disagree about who can be classified as an ecotourist and there is little statistical data, some estimate that more than five million ecotourists—the majority of the ecotourist population—come from the United Stateswith many others from Western Europe, Canada and Australia. Currently, there are various moves to create national and international ecotourism accreditation programs, although the process is also controversial. Ecotourism is a late 20th-century neologism compounded from eco- and tourism.
According to the Oxford English Dictionaryecotour was first recorded in and ecotourism»probably after ecotour «, in One source claims the terms were used earlier. Several ecolabels on tourism exist. Ecotourism in both terrestrial and marine ecosystems can benefit conservation, provided the complexities of history, culture, and ecology in the affected regions are successfully navigated.
Because the regulation of ecotourism may be poorly implemented, ecologically destructive greenwashed operations like underwater hotels, helicopter tours, and wildlife theme parks can be categorized as ecotourism along with canoeing, camping, photography, and wildlife observation. The failure to acknowledge responsible, low-impact ecotourism puts legitimate ecotourism companies at a competitive disadvantage.
Many environmentalists have argued for a global standard of accreditation, differentiating ecotourism companies based on their level of environmental commitment, creating a standard to follow. A national or international regulatory board would enforce accreditation procedures, with representation from various groups including governments, hotels, tour operators, travel agents, guides, airlines, local authorities, conservation organizations, and non-governmental organizations.
Crinion suggests a Green Stars System, based on criteria including a management plan, benefit for the local community, small group interaction, education value and staff training. Environmental impact assessments could also be used as a form of accreditation. Feasibility is evaluated from a scientific basis, and recommendations could be made to optimally plan infrastructure, set tourist capacity, and manage the ecology.
This form of accreditation is more sensitive to site specific conditions. Some countries have their own certification programs for ecotourism. Costa Rica, for example, runs the Certification of Sustainable Tourism CST program, which is intended to balance the effect that business has on the local environment.
The CST program focuses on a company’s interaction with natural and cultural resources, the improvement of quality of life within local communities, and the economic contribution to other programs of national development. CST uses a rating system that categorizes a company based upon how sustainable its operations are.
Based upon these criteria, the company is evaluated for the strength of its sustainability. The measurement index goes from 0 to 5, with 0 being the worst and 5 being the best. An environmental protection strategy must address the issue of ecotourists removed from the cause-and-effect of their actions on the environment. More initiatives should be carried out to improve their awareness, sensitize them to environmental issues, and care about the places they visit.
Tour guides are an obvious and direct medium to communicate awareness. With the confidence of ecotourists and intimate knowledge of the environment, tour guides can actively discuss conservation issues.
Informing ecotourists about how their actions on the trip can negatively impact their environment and the local people. A tour guide training program in Costa Rica’s Tortuguero National Park has helped mitigate negative environmental impacts by providing information and regulating tourists on the parks’ beaches used by nesting endangered sea turtles.
The underdevelopment theory of tourism describes a new form of imperialism by multinational corporations that control ecotourism resources.
These corporations finance and profit from the development of large scale ecotourism that causes excessive environmental degradation, loss of traditional culture and way of life, and exploitation of local labor. In Zimbabwe and Nepal’s Annapurna region, where underdevelopment is taking place, more than 90 percent of ecotourism revenues are expatriated to the parent countries, and less than 5 percent go into local communities. The lack of sustainability highlights the need for small scale, slow growth, and locally based ecotourism.
Local peoples have a vested interest in the well-being of their community, and are therefore more accountable to environmental protection than multinational corporations, though they receive very little of the profits. The lack of control, westernization, adverse impacts to the environment, loss of culture and traditions outweigh the benefits of establishing large scale ecotourism. Additionally, culture loss can be attributed to cultural commodification, in which local cultures are commodified in order to make a profit.
The increased contributions of communities to locally managed ecotourism create viable economic opportunities, including high-level management positions, and reduce environmental issues associated with poverty and unemployment.
Because the ecotourism experience is marketed to a different lifestyle from large scale ecotourism, the development of facilities and infrastructure does not need to conform to corporate Western tourism standards, and can be much simpler and less expensive. Profits accrue locally and import leakages are reduced. When such investments are required, it is crucial for communities to find a company or non-governmental organization that reflects the philosophy of ecotourism; sensitive to their concerns and willing to cooperate at the expense of profit.
The basic assumption of the multiplier effect is that the economy starts off with unused resources, for example, that many workers are cyclically unemployed and much of industrial capacity is sitting idle or incompletely utilized. By increasing demand in the economy, it is then possible to boost production. If the economy was already at full employment, with only structural, frictional, or other supply-side types of unemployment, any attempt to boost demand would only lead to inflation.
For various laissez-faire schools of economics which embrace Say’s Law and deny the possibility of Keynesian inefficiency and under-employment of resources, therefore, the multiplier concept is irrelevant or wrong-headed. This sum would go to the road builders, who would hire more workers and distribute the money as wages and profits. The households receiving these incomes will save part of the money and spend the rest on consumer goods.
These expenditures, in turn, will generate more jobs, wages, and profits, and so on with the income and spending circulating around the economy. The multiplier effect arises because of the induced increases in consumer spending which occur due to the increased incomes — and because of the feedback into increasing business revenues, jobs, and income.
This process does not lead to an economic explosion not only because of the supply-side barriers at potential output full employment but because at each «round», the increase in consumer spending is less than the increase in consumer incomes.
That is, the marginal propensity to consume MPC is less than one, so that each round some extra income goes into saving, leaking out of the cumulative process.
Each increase in spending is thus smaller than that of the previous round, preventing an explosion. Some of the world’s most exceptional biodiversity is located in the Galapagos Islands. IGTOA is a non-profit dedicated to preserving this unique living laboratory against the challenges of invasive species, human impact, and tourism. Natural resource management can be utilized as a specialized tool for the development of ecotourism.
There are several places throughout the world where a number of natural resources are abundant, but with human encroachment and habitats, these resources are depleting. Without the sustainable use of certain resources, they are destroyed, and floral and faunal species are becoming extinct. Ecotourism programs can be introduced for the conservation of these resources. Several plans and proper management programs can be introduced so that these resources remain untouched, and there are many organizations—including nonprofits—and scientists working on this field.
Natural resources of hill areas like Kurseong in West Bengal are plenty in number with various flora and fauna, but tourism for business purpose poised the situation. Researchers from Jadavpur University are presently working in this area for the development of ecotourism to be used as a tool for natural resource management.
In Southeast Asia government and nongovernmental organizations are working together with academics and industry operators to spread the economic benefits of tourism into the kampungs and villages of the region.
Asummit held in Quebec led to the Global Sustainable Tourism Criteria—a collaborative effort between the UN Foundation and other advocacy groups. The criteria, which are voluntary, involve the following standards: «effective sustainability planning, maximum social and economic benefits for local communities, minimum negative impacts on cultural heritage, and minimum negative impacts on the environment.
In the continuum of tourism activities that stretch from conventional tourism to ecotourism, there has been a lot of contention to the limit at which biodiversity preservation, local social-economic benefits, and environmental impact can be considered «ecotourism».
For this reason, environmentalists, special interest groups, and governments define ecotourism differently. Environmental organizations have generally insisted that ecotourism is nature-based, sustainably managed, conservation supporting, and environmentally educated. The problems associated with defining ecotourism have often led to confusion among tourists and academics.
Many problems are also subject of considerable public controversy and concern because of green washinga trend towards the commercialization of tourism schemes disguised as sustainable, nature based, and environmentally friendly ecotourism. They are also morally disconcerting because they mislead tourists and manipulate their concerns for the environment. Even if some of the guidelines are being executed, the local communities are still facing many of the negative impacts. South Africa is one of the countries that is reaping significant economic benefits from ecotourism, but the negative effects far outweigh the positive—including forcing people to leave their homes, gross violations of fundamental rights, and environmental hazards —far outweigh the medium-term economic benefits.
Ecotourism channels resources away from other projects that could contribute more sustainable and realistic solutions to pressing social and environmental problems. Indeed, many argue repeatedly that ecotourism is neither ecologically nor socially beneficial, yet it persists as a strategy for conservation and development [34] due to the large profits.
While several studies are being done on ways to improve the ecotourism structure, some argue that these examples provide a rationale for stopping it altogether. The ecotourism system exercises tremendous financial and political influence.
The evidence above shows that a strong case exists for restraining such activities in certain locations. Funding could be used for field studies aimed at finding alternative solutions to tourism and the diverse problems Africa faces in result of urbanization, industrialization, and the overexploitation of agriculture. In this case, ecotourism has harmed the environment and local people and has led to conflicts over profit distribution.
In a perfect world, more efforts would be government using ecotourism as a way to make money towards educating tourists of the environmental and social effects of their travels. Very few regulations or laws stand in place as boundaries for the investors in ecotourism. These should be implemented to prohibit the promotion of unsustainable ecotourism projects and materials which project false images of destinations, demeaning local and indigenous culture. Though conservation efforts in East Africa are indisputably serving the interests of tourism in the region it is important to make the distinction between conservation acts and the tourism industry.
Conservation in the Northwest Yunnan Region of China has similarly brought drastic changes to traditional land use in the region.
Can eco-tourism help save the ocean? — The Economist
Models of Ecotourism. Ecotourism in Australia:. Killing Two Birds with One Stone. Mney Jaimi Gregory. Around the world, terrestrial ecosystems are becoming farmland ecotourlsm are falling victim to suburban housing developments, highways, and continuously expanding cities.
chapter and author info
Many species are on the verge of extinction and their natural habitats are falling to this increased industrialization. The decreasing existence of biodiversity is a worldwide concern, however some suggest makf the extent of this biodiversity problem is not fully realized by the majority of the population. Consequently, our ecotourksm need for preserved ecosystems has been realized by many countries. The realization of this need by these economically-driven countries has acted as a catalyst for the innovation of a business called «ecotourism». The purpose of ecotourism is to create incentive to preserve ecosystems while at governmrnt same time gaining economic profit. In essence, ecotourism is a business that has the potential for not only helping. Ecotourism is an important topic to study because of its growing influence on tourist travel. On the global scale, we see that ecotourism is moving up on the charts as a desirable activity- and one that is making an economic impact. Although the tourism business is notorious for its somewhat questionable statistics, it would be fair to say that ecotourism is making an economic impact globally. Some suggest that it seems that ecotourism could be the fastest growing part of it. Among world leaders in ecotourism, Australia is prominent due to the beauty of its native grasslands, its wetlands, and the diversity of its wildlife.
Comments
Post a Comment